CW DATE:
TITLE:
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:
CW DATE:
September 2018
TITLE: What is the Weather?
Source sheet - HERE
ENTRY TASK:
Look outside the window in your class. What is the weather like? (Try to give lots of detail).
Circle the terms below that most closely describe today's weather.
If you want to add different words… there is space at the bottom of the table.
Hot
|
Cold
|
Warm
|
Windy
|
Calm
|
Dry
|
Rainy
|
Sunny
|
Cloudy
|
Breezy
|
Foggy
|
Clear
|
Cool
|
Snowy
|
Frosty
|
Humid
|
KEY TERMS:
Weather - What is happening outside in the air around us. It can change from hour to hour!
Examples of weather - Photo Album







 ACTIVITIES:
ACTIVITIES:1. Match up the cartoons below with the photos that they best represent... cut out the cartoons and stick them to the photos.
Note: there are six cartoons and eight photos, so two photos may not have a cartoon :)
In this first Study Unit of Year 8, we are going to be investigating weather... what it is, different types, why it happens and how we can measure and even predict it.
To start us of, you are going to make a Title Page about weather. So, using what you have learned today and other ideas that you have about the weather PLAN, DRAFT and DRAW a title page about the topic of WEATHER.
TIPS:
Use a pencil for drawing and plenty of colour to make your page striking.
Try to cover your whole page… this often gives a great effect.
Use the plain paper provided
Sketch out your idea on one piece of paper first… then use a fresh piece of paper to draw your final version.
PLENARY:
Sometimes, one type of weather is often linked to another... for example, if it is SUNNY... it is often WARM. Can you think of any other types of weather that are linked?
Further Learning:
Check out a weather report between now and next lesson... for example on the TV, WWW, Radio, or in a Newspaper. Does it mention any types of weather we did not think of today?
NL: to finish title page/stick etc... interrupted by fire drill on Monday
Starter... 26th Sept 18
Listen carefully...
- Rain vid/audio linke - HERE
Questions:
- What is it that you can hear?
- What type of rain is it? - describe.
- Can you suggest whether it has been raining for a long time or a short time? Explain.
- Can you hear anything else... or are there things that you cannot hear that give us more information about this rain event?
CW DATE: 26th September 2018
TITLE:
What is Rain?
ENTRY TASK:
What actually is rain? Where does it come from?
KEY TERMS:
Evaporation - when liquid turns into a gas
Condensation - when gas turns into a liquid
Video extract - HERE (from 1:16)
Cycle - a series of transfers that follow a circular pattern
Met Office Video - HERE
Questions?
ACTIVITIES:
1.
Which description goes with which term? (Read and remember/recall):
Evaporation -
Condensation -
....................... heating can change liquid water into an invisible vapor or gas.
........................cooling causes water vapor (a gas) to turn back into liquid
Copy the above.
What is a "Cycle"?
Water Cycle
Source Sheet: HERE (print pp 1 and 3 only)
PLENARY:
Spellings...
Can you suggest why?
HW:
CW DATE: 1st October 2018
TITLE:
Why does it Rain?
ENTRY TASK:
Cut and sequence Flow diagram annotations to describe the water cycle (See pp 1 of source sheet HERE)
KEY TERMS:
Flow Diagram -

Diagrams that are used to show a sequence of events and interconnections.
Precipitation - (In weather) Water in liquid or solid form falling clouds
 Transpiration - The process in which water vapour is released by plants into the atmosphere.
Transpiration - The process in which water vapour is released by plants into the atmosphere.ACTIVITIES: Review and complete next lesson (leaves and magnifying glasses)
1. Class reading of pp 2 of source sheet and discussion.
2. Colour the precipitation picture and discuss the differences.
3. Add "Precipitation" to the Water Cycle diagram from last lesson.
4. Study the Transpiration information... complete the outline sketch (pp 3 and 4 source sheet - PO pp4 for students).
PLENARY:
Magnifying glasses... go find stomata on leaves.
or
Which is likely to have more moisture (water vapor) in it... Warm or Cold air?
Can you suggest why?
What are two ways that water can get into the air?
HW:
CW DATE: 10th October 2018
TITLE:
Types of Rain
ENTRY TASK:
Transpiration... Leaves
INTRODUCTION
Video: Expanding and contracting (shrinking) air due to temperature change - HERE
- When air is heated, it expands, becomes lighter and begins to rise.
- If there is water vapour (due to evaporation) in it, that will rise too.
- Higher up in the Atmosphere, the surrounding air is colder.
- This cools the rising warm air which shrinks and becomes heavier.
- As the air cools down and shrinks, it cannot hold onto all the water vapour it is carrying... so some of it is released by condensation.
KEY TERMS:
Convection - Rising air caused by heating, expansion and becoming lighter.
Relief - the physical shape of the land eg high, low, steep or flat.
ACTIVITIES:
See the source sheet - Here (page 2, 3, 4)
Completed Convection Rain... onto Relief Rain next lesson. Sheet in folder...
PLENARY:
Give three things lead to rain?
HW:
After half term... measuring the weather. iCt room booked... plan a lesson to collect some data, input into a spread sheet and make a graph... follow up report...
CW DATE: 31st October 2018
TITLE:
Halloween Weather Forecast using Data
ENTRY TASK:
Halloween - Who is going Trick or Treating?
So... how useful would it be to know what the weather will be like?
INTRODUCTION
A weather FORECAST attempts to PREDICT what the weather will be like over the following few hours or days.
Using the data below, you can make a prediction of the weather for this evening…
Study the data shown in the table… Summarise the changes predicted in the right hand column
KEY TERMS:
Forecast - a prediction of something that is expected to happen in the future. For example a weather forecast predicts the weather that is expected over the next few hours or days.
ACTIVITIES:
Source sheet - HERE
This takes students through...
a) Manual summarising of weather data (using the table of pp1.
Time
|
5pm
|
6pm
|
7pm
|
8pm
|
9pm
|
10pm
|
11pm
|
Summary of change
| |
Temperature (Deg C)
|
10
|
10
|
9
|
8
|
8
|
9
|
10
| ||
Cloud
|
Cloudy
|
Patchy
|
Patchy
|
Cloudy
|
Cloudy
|
Cloudy
|
Thick Cloud
| ||
Precipitation Chance (%)
|
5
|
5
|
5
|
10
|
10
|
40
|
40
| ||
Wind Direction
|
From the ESE
|
From the ESE
|
From the ESE
|
From the ESE
|
From the ESE
|
From the ESE
|
From the ESE
| ||
Wind Speed
|
6
|
6
|
5
|
5
|
5
|
5
|
5
| ||
Humidity (amount of moisture in the air as %)
|
71
|
76
|
79
|
82
|
85
|
88
|
91
| ||
Most important changes
| |||||||||
b) Completion of a google sheet for the same data (Layout HERE)
c) Use of the data on the google sheet in the production of graphs to show key predictions for Trick or Treating Weather.
d) Follow on will be to copy the graphs into a document and to write a weather forecast based on these.
PLENARY:
HW:
CW DATE: 5th November 2018
TITLE:
Reporting your weather observations
ENTRY TASK:
Find and review the google sheet with your weather data and graphs showing selected aspects of the weather on Halloween.
Choose two graphs to use for today's reporting lesson.
INTRODUCTION
Having gathered information, processed and presented it (eg in graphs), we often need to report what we have found by combining our data and graphs and adding a written narrative about it. The aim is to make it easier for other people to understand what you have found.
KEY TERMS:
Report - to give a spoken or written account of something that one has observed, heard, done, or investigated.
ACTIVITIES:
1. Find and open the Weather Report document assigned to you in Google Classroom.
Copy - HERE
2. Copy (Ctrl + C) and paste (Ctrl + V) your data table and graphs to the Report document.
3. Write a commentary about each graph that...
a. Describes what it shows
b. Suggests how the changes or weather conditions you have described will affect people out and about over the course of that evening.
PLENARY:
HW:
CW DATE: 14th November 2018
TITLE:
Weather Learning Check
ENTRY TASK:
Sign on to:
a. Google Classroom
b. Kerboodle
INTRODUCTION
In our learning check today there are two types of assessment...
one is on kerboodle and is interactive where you have multiple choice questions and some sequencing activities...
...the other is on Google Classroom where you will be able to demonstrate your weather description skills by completing two graph interpretation exercises.
For these activities, you need to sit apart from each other... because I want to know what you can do
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
First:
Google Classroom activities - HERE
You need to click "HAND IN" when done.Paper copy available for drafting.
"Walk through" the paper.
Second:
Kerboodle Activities 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 - HERE
You will get immediate feedback on these :)
Independent
PLENARY:
HW:
CW DATE: 19th November 2018
TITLE:
From Weather to Climate
ENTRY TASK:
Who can remember the definition of "weather"... a clue: Look out of the window!
INTRODUCTION
When we are thinking about the weather, we consider the day to day or hour to hour condition of the atmosphere... it is short term.
What about if I asked you what the Summer is like in the UK... or what the conditions in the Saharah Desert are like?
When we think about weather that we might expect in a certain place and at a certain time of year, we are actually thinking about CLIMATE!
KEY TERMS:
Climate - The long term, expected weather conditions for a specific place and time (Usually this is based on weather observations made over at least 30 years which are used to calculate averages).
ACTIVITIES:
 1. Calculating Averages and using them to investigate UK Climate - HERE
1. Calculating Averages and using them to investigate UK Climate - HEREWe could also add a line to show the Average values eg for 1960 to 1989... why might that be useful?
PLENARY:
CW DATE:
TITLE:
Climate Zones
Source - HERE
ENTRY TASK:
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
PLENARY:
HW:
CW DATE:
3rd December 2018
TITLE:
What causes different climates in different parts of the World?
Source - HERE
ENTRY TASK:
Check your World Climate Maps from last lesson and the Key that goes with it.
INTRODUCTION
KEY TERMS:
Latitude - Imaginary lines that divide the world into Horizontal "layers"...
(If does not open... access via alternative - school -account)
ACTIVITIES:
See source sheet
PLENARY:
HW:
CW DATE: 9th January 2019
TITLE:
Climates around the World - Review
Source sheet - HERE
ENTRY TASK:
Video extract: HERE
(Upto 2min 59secs)
INTRODUCTION
In today's learning we will explore one of the key factors that causes differences in the climates of places at different latitudes.
KEY TERMS:
Climate - The average expected weather conditions for a specific place at a specific time of year.
Latitude - The distance from the equator.
ACTIVITIES:
Complete the worksheet provided. (Sheet - HERE)
PLENARY:
Feedback ideas for an experiment.
or
View remainder of video
HW:
CW DATE: 14th January 2019
TITLE: Climate Change
ENTRY TASK:
Complete "Climate around the World" sheet 5.10
INTRODUCTION
Study the graph shown on page 91 of the Geog 2 text book.
What does it reveal about the Earth's Climate over time?
KEY TERMS:
ACTIVITIES:
Reading together: pp 90/91 of the text.
Complete the sheet (6.1)
Using the graph and cartoons on page 91, explain what is happening at A to E

Using the map extract, shade the areas that would be affected by the melting of
Complete the sheet (6.1)
Using the graph and cartoons on page 91, explain what is happening at A to E
Using the map extract, shade the areas that would be affected by the melting of
- The Greenland Ice Sheet.
- The Antarctic Ice Sheet.
- Find out how far above sea level you live.
Use the "Did you know" points on pp 89 to help you...

Adapted...

PLENARY:
HW:
CW DATE: 23rd January 2019
TITLE:
The causes of climate change on Earth.
ENTRY TASK:
Evidence tells us that the climate on earth has ................. many times. Sometimes it has been much ............... than today, at other times much warmer. The very coldest episodes are called
....... ............ when large areas of the planets surface were covered in ice sheets (sometimes kilometers thick). Today we are in an "............................", a period between ice ages. This began in the UK only about 10,000 to 11,000 years BP (Before Present)
WORDBOX
ICE AGES changed INTERGLACIAL colder
INTRODUCTION
In today's lesson we will be exploring some of the causes of climate change affecting Earth.
Scientists have studied the causes of climate change and recognise, that in the past these were natural. Today, however, most experts agree that humans are having a large impact on our climates... they have concluded the following things:

KEY TERMS:
Global Warming - A pattern of consistent increases in the average temperature of the Earth
Climate Change - Periodic rises and falls in the average climate of the planet in which temperatures either rise or fall.
Greenhouse Gasses - Gasses that accumulate in the upper atmosphere and act to retain heat.
Axial Tilt - The tilt of the earth on its axis of rotation so that it spins at a few degrees off of vertical.
ACTIVITIES:
1. How does the NATURAL Greenhouse effect work?
Drawing GH effect diagram...
Done... onto task below, but not to redraw! Could be a written activity (literacy targets)...
2. How have people changed and increased the Greenhouse Effect? As we work through the explanation, make your own key point list... you should be able to tell me if something is key (and we will write it on the board).
Adding the Anthropogenic component...
First... some AV...
Causes and consequences - Nat Geog HERE
Pollutants HERE

Key facts:
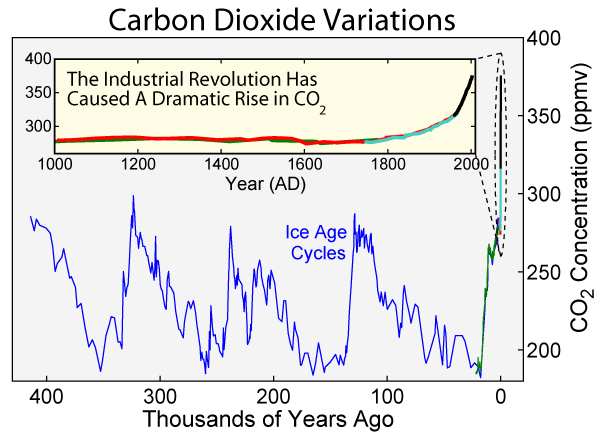

3. What is the evidence that people are responsible for the recent changes (Correlation pp 92 - Changes in Global Temperature since 1850 relative to the average temperature 1961 to 1991):

4. What evidence is there that Climate Change is happening?
PP 96/7
a. Describe and explain two pieces of evidence that appear to prove that Climate Change is already happening.
b. Write a conclusion to outline how technological change and the use of new resources in the 1800s is affecting Polar Bears in the Arctic.
c. Draw a picture to go with your conclusion.
PLENARY:
HW:
TITLE:
The causes of climate change on Earth.
ENTRY TASK:
Evidence tells us that the climate on earth has ................. many times. Sometimes it has been much ............... than today, at other times much warmer. The very coldest episodes are called
....... ............ when large areas of the planets surface were covered in ice sheets (sometimes kilometers thick). Today we are in an "............................", a period between ice ages. This began in the UK only about 10,000 to 11,000 years BP (Before Present)
WORDBOX
ICE AGES changed INTERGLACIAL colder
INTRODUCTION
In today's lesson we will be exploring some of the causes of climate change affecting Earth.
Scientists have studied the causes of climate change and recognise, that in the past these were natural. Today, however, most experts agree that humans are having a large impact on our climates... they have concluded the following things:
KEY TERMS:
Global Warming - A pattern of consistent increases in the average temperature of the Earth
Climate Change - Periodic rises and falls in the average climate of the planet in which temperatures either rise or fall.
Greenhouse Gasses - Gasses that accumulate in the upper atmosphere and act to retain heat.
Axial Tilt - The tilt of the earth on its axis of rotation so that it spins at a few degrees off of vertical.
ACTIVITIES:
1. How does the NATURAL Greenhouse effect work?
Drawing GH effect diagram...
Done... onto task below, but not to redraw! Could be a written activity (literacy targets)...
2. How have people changed and increased the Greenhouse Effect? As we work through the explanation, make your own key point list... you should be able to tell me if something is key (and we will write it on the board).
Adding the Anthropogenic component...
First... some AV...
Causes and consequences - Nat Geog HERE
Pollutants HERE

Key facts:
- Thomas Newcomen in 1712 invented an effective steam engine using coal as fuel (coal releases Co2 when it is burned).
- James Watt in 1776 improved the efficiency of Newcomen's engine making it more popular!
- Industrial Revolution in the UK - from 1850, further advances in industry saw the widespread use of coal fired engines in pumping water, rail transport, ships and in factory machines.
- Since the Industrial Revolution, we have put so much extra Co2 into the atmosphere (along with a bunch of other pollutants) that the climate was affected...
What do the graphs show... notice the correlation from around 1850 in both CO2 levels and global temperature!

- Many pollutants, including Co2 are also Greenhouse Gases. These have built up in the Upper Atmosphere trapping more heat in the Earth's system... the result... Global Warming due to an ENHANCED GREENHOUSE EFFECT!
Video: HERE (Enhanced Greenhouse Effect)
Task: in your own words...
4. What evidence is there that Climate Change is happening?
PP 96/7
a. Describe and explain two pieces of evidence that appear to prove that Climate Change is already happening.
b. Write a conclusion to outline how technological change and the use of new resources in the 1800s is affecting Polar Bears in the Arctic.
c. Draw a picture to go with your conclusion.
PLENARY:
HW:
27th Feb 2019 - Postponed as DVD player not working!
"The Day After Tomorrow" - Lit Exercise
Movie Review
1. What is the theme of the movie?
2. Characters
- These will be introduced to viewers in the first few minutes of the movie.
- Names + Role in the movie
- How are the characters linked?
3. Summary of the Story
It is a long movie and the story will unfold gradually.
As the movie progresses, stop periodically and jot down 3 to 4 bullet points of no more than one line each, of key events in the story.
4. Comments and opinions
Jot down how enjoyable/entertaining the movie is and why.
At the end of the movie, we will edit and then use the notes to write a review.
In it we will ensure that caps and punctuation is correctly employed and that spellings are checked.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.